Colour
Grading White Diamonds
The majority of diamonds that are mined are in a range of pale yellow or brown colour that is termed the normal colour range. Diamonds that are of intense yellow or brown, or any other colour are called fancy colour diamonds. Diamonds that are of the very highest purity are totally colourless, and appear a bright white. The degree to which diamonds exhibit body colour is one of the four value factors by which diamonds are assessed.
History of Colour Grading
Colour grading of diamonds was performed as a step of sorting rough diamonds for sale by the London Diamond Syndicate.
As the diamond trade developed, early diamond grades were introduced by various parties in the diamond trade. Without any co-operative development these early grading systems lacked standard nomenclature, and consistency. Some early grading scales were; I, II, III; A, AA, AAA; A, B, C. Numerous terms developed to describe diamonds of particular colours: golconda, river, jagers, cape, blue white, fine white, and gem blue, “brown”.
Grading the Normal Colour Range
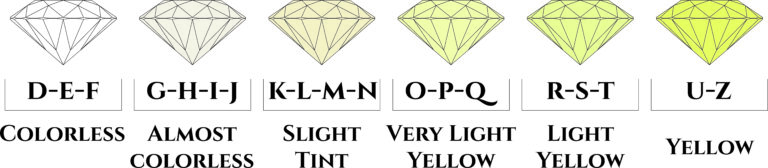
Refers to a grading scale for diamonds in the normal colour range used by internationally recognized laboratories (AGI for example). The scale ranges from D which is totally colourless to Z which is a pale yellow or brown colour. Brown diamonds darker than K colour are usually described using their letter grade, and a descriptive phrase, for example M Faint Brown. Diamonds with more depth of colour than Z colour fall into the fancy colour diamond range.
Diamond colour is graded by comparing a sample stone to a masterstone set of diamonds. Each masterstone is known to exhibit the very least amount of body colour that a diamond in that colour grade may exhibit. When sample stones are compared with the master stone, the grader assesses whether the sample has more, less or equal colour to the masterstones.
A grading laboratory will possess a complete set of masterstones representing every colour grade. However, the independent grader working in a retail will possess a range of masterstones that covers only the typical grade range of colour they expect to encounter while grading.
A typical grading set of masterstones would consist of five diamonds in two grade increments, such as an E, G, I, K, and M. It is not common for a grader to possess a D masterstone, as the E masterstone is more useful in dividing the D and E colour grades. The intermediate grades are assessed by the graders judgement.
Diamonds in the normal colour range are graded loose, with the table facet facing downward and pavilion side upwards. When colour grading is done in the mounting, other techniques will apply and the grade will usually be expressed as a range (for example F-G)
“D” colour has a unique “icy” look to it. Diamonds that rate toward the colourless end of the range are sometimes known as “high-colour” diamonds, and those toward the other end, “low-colour” diamonds. These terms refer to the relative desirability (as demonstrated by market prices) of colour grades, not the intensity of the colour itself.
The agi Colour Grading Scale
| Grade | Category |
| D | Colourless |
| E | |
| F | |
| G | Near Colourless |
| H | |
| I | |
| J | |
| K | Faint Yellow |
| L | |
| M | |
| N | Very Light Yellow |
| O | |
| P | |
| Q | |
| R | |
| S | Light Yellow |
| T | |
| U | |
| V | |
| W | |
| X | |
| Y | |
| Z | |
| FANCY | Fancy Colour |